36 rows Glycogen storage disease type 1A is characterized by growth retardation. They may be treated orally using their oral emergency regimen click here generally give 200ml of a 25 glucose polymer solution every 2 hours but assess very carefully.
Glycogen Storage Disease Article
How is Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1a Treated.
How to treat glycogen storage disease type 1a. How is glycogen storage disease treated in a child. Glycogen storage disease type I also known as GSDI or von Gierke disease is an inherited disorder caused by the buildup of a complex sugar called glycogen in the bodys cells. While GSD type IV is a clinically heterogeneous disorder that severely affects liver andor muscle APBD is a late-onset slowly.
Type I Von Gierke disease this is the most common type of glycogen storage disease and accounts for 90 of all glycogen storage disease cases. Lipid-lowering medications for elevated lipid levels despite good metabolic control. Glycogen storage disease type IA GSDIa is a severe metabolic disease that can be fatal in early childhood if not treated.
Medical nutritional therapy to maintain normal blood glucose levels prevent hypoglycemia and provide optimal nutrition for growth and development. Dietary management is the only effective treatment for GSDIa and will allow survival into adulthood however only some of the symptoms of the disease may be prevented using these methods. Genetic Disorder-Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1 GSD I or Von Gierkes Disease as stated is an inherited medical condition.
In general no specific treatment exists to cure glycogen storage diseases GSDs. Types of Glycogen Storage Disease. Molecular genetic testing for the G6PC and SLC37A4 genes is available to confirm a diagnosis.
For types I III and IV your childs healthcare provider may suggest a special diet to help control symptoms. The primary goal of treatment is to correct hypoglycemia and maintain a normoglycemic state. Type II Pompes disease acid maltase deficiency.
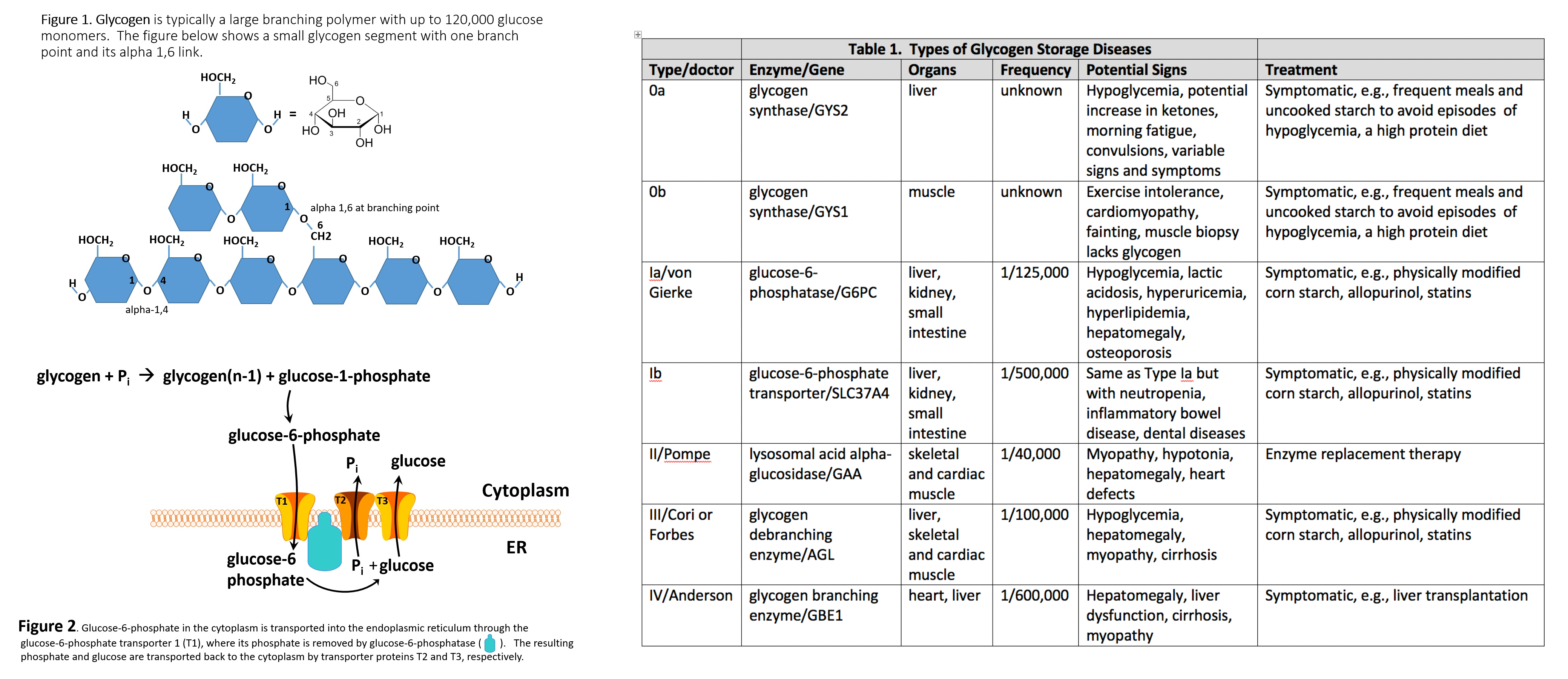
Allopurinol to prevent gout when dietary therapy fails to completely normalize blood uric acid concentration. GSD type I is diagnosed by laboratory tests that indicate abnormal levels of glucose lactate uric acid triglycerides and cholesterol. Glycogen storage disease type I GSDI is characterized by accumulation of glycogen and fat in the liver and kidneys resulting in hepatomegaly and renomegaly.
Liver transplantation is an option for some patients. GSD type I. Glycogen storage disease type 1a is a condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels enlarged liver and kidneys and impaired growth that results from the build-up of stored glycogen in the body.
The accumulation of glycogen in certain organs and tissues especially the liver kidneys and small intestines impairs their ability to function normally. The main types of glycogen storage diseases in children are categorized by number and name. The two subtypes GSDIa and GSDIb are clinically indistinguishable.
People with GSD type Ia should avoid foods with sucrose table sugar fructose sugar from fruits and lactose and galactose sugars found in milk. The treatment of GSD type Ia involves a careful monitoring of the affected persons diet both in frequency of meals and type of foods eaten. Autosomal recessive genetic disorder results in lack of enzyme glucose-6-phosphatas.
If the patient is obviously unwell they must be treated with intravenous fluids. How is Glycogen Storage Disease Type IA Treated. Patients with neutropenia benefit from treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.
The main symptoms can be treated with strict dietary management. Your child may also have to take certain medicines. Treatment will vary depending on what type of GSD your child has.
Glycogen storage disease type IV Andersen disease OMIM 232500 and Adult Polyglucosan Body Disease APBD OMIM 263570 are allelic disorders caused by a deficiency of the glycogen branching enzyme encoded by the GBE1 gene. INITIAL INVESTIGATIONS Blood pH and gases Glucose Urea electrolytes. It is recommended that patients with type 1 glycogen storage disease be referred to a facility that is experienced in treating children with metabolic diseases.
The enzyme influences liver cell to breakdown glycogen to glucose to maintain constant normal blood sugar level. The normoglycemic state can be achieved with overnight nasogastric infusion of. In some cases diet therapy is helpful.
Molecular genetic testing can also be used for carrier testing and prenatal diagnosis. Enzyme Glucose-6-Phosphatase Deficiency 1.

Glycogen Storage Diseases Download Table
Glycogen Storage Disease Type I Wikiwand

High Prevalence Of Fractures In Glycogen Storage Disease Type I Gsd I R M Van Der Ende D H Martens G P A Smit T G J Derks E Van Der Veer Rixt Ppt Download

Foods Allowed And Foods Not Allowed In Gsd I Download Table

Pin On Glycogen Storage Disease

Von Gierke Disease Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis

Diagnosis And Management Of Glycogen Storage Disease Type I A Practice Guideline Of The American College Of Medical Genetics And Genomics Genetics In Medicine
Glycogen Storage Disease Type I Gsd I
Glycogen Storage Disease Types Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
0 comments:
Post a Comment