Clinical presentation diagnosis treatment and outcome. Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia NCAH is one of the most frequent autosomal recessive disorders in man with a prevalence ranging from 01 in Caucasians up to a few percent in certain ethnic groups.
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Prezentaciya Onlajn
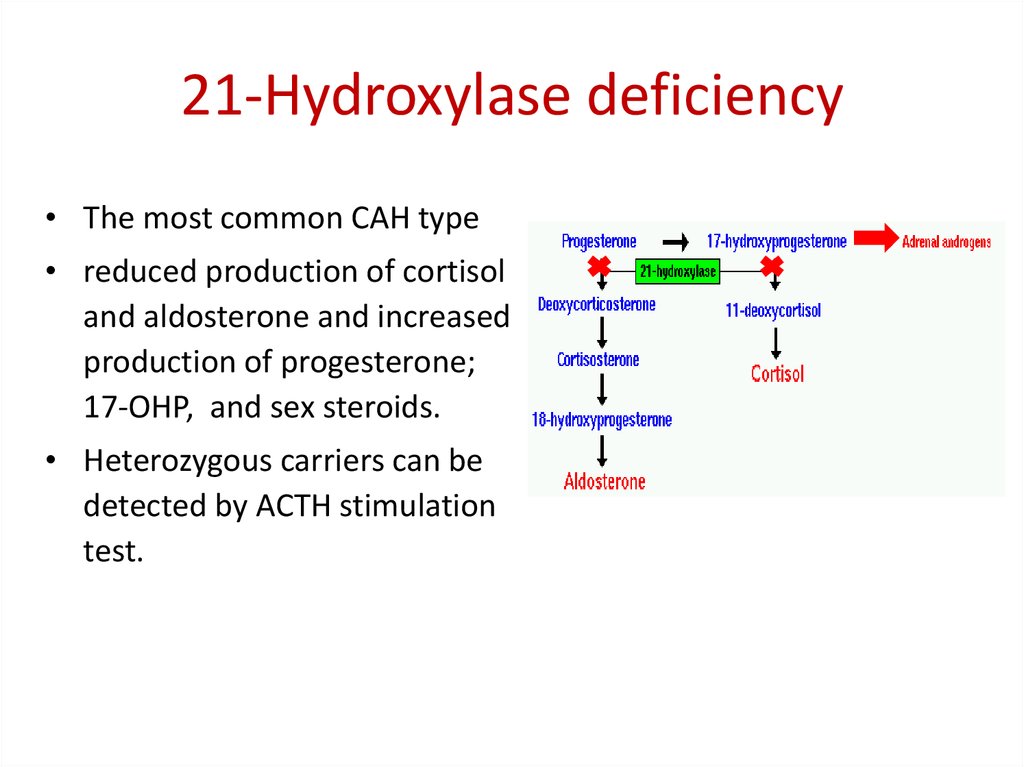
Defective conversion of 17-hydroxyprogesterone to 11-deoxycortisol accounts for more than 90 percent of cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia 1.

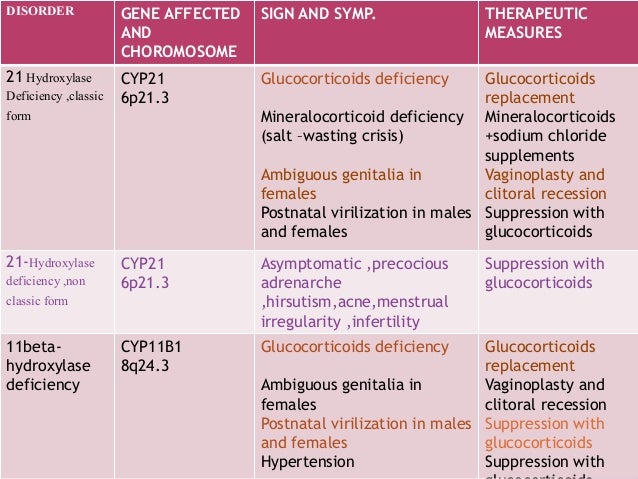
Treatment 21 hydroxylase deficiency. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the CYP21A2 gene. Many are asymptomatic throughout their lives although symptoms may develop during puberty after puberty or post partum. 21 hydroxylase deficiency Endocrine Treatment Cortisol treatment can come in the form of tablets or suspension.
In some cases people affected by non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency NCAH may not require any treatment. Oral cortisol is often destroyed by gastric acids that is why it is necessary to have the treatment dose doubled as compared to the normal cortisol production. Infants identified at birth with 21-hydroxylase deficiency are treated with hormones and steroids to prevent a salt-wasting crisis.
Prenatal treatment of 21-OHD CAH lessens the high-level androgen exposure to the brain during sexual differentiation as well as minimizing the degree of genital virilization in affected female. The goals of treatment are to manage to symptoms. Patients with classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency require long-term glucocorticoid treatment to inhibit excessive secretion of CRH and ACTH and reduce the abnormally high serum concentrations of adrenal androgens.
It is imperative to make the diagnosis of 21-OHD CAH as quickly as possible in order to initiate therapy and arrest the effects of cortisol deficiency and mineralocorticoid deficiency if present. This conversion is mediated by 21-hydroxylase or in current terminology P450 21A2 encoded by the CYP21A2 gene. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency 2014 revision Purpose of developing the guidelines.
The goals of treatment are to manage to symptoms. Approximately 75 of 21-OHD cases have the serious SW type 1 9 10. In childhood and adulthood other medications may be used to improve growth and fertility.
21-hydroxylase deficiency in Japan 79 with salt-wasting SW or simple virilizing SV disease. And serious SW may be fatal. The first guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency 21-OHD were published as a diagnostic handbook in Japan in.
There are currently limited trials comparing the efficacy and safety of different glucocorticoid replacement regimens for treating 21-hydroxylase deficiency CAH in children and adults and we were unable to draw any firm conclusions based on the evidence that was presented in the included trials. This results in 1 impaired cortisol biosynthesis and adrenal insufficiency and 2. Treatment for 21-hydroxylase deficiency depends on the severity of symptoms and the form of the condition.
Due to the timing of genital development oral treatment with dexamethasone begins at 4 weeks gestation even before determination of sex and presence of disease genes in the fetus. Females affected are virilised at birth and are at risk for genital ambiguity. Treatment of nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency depends on symptoms.
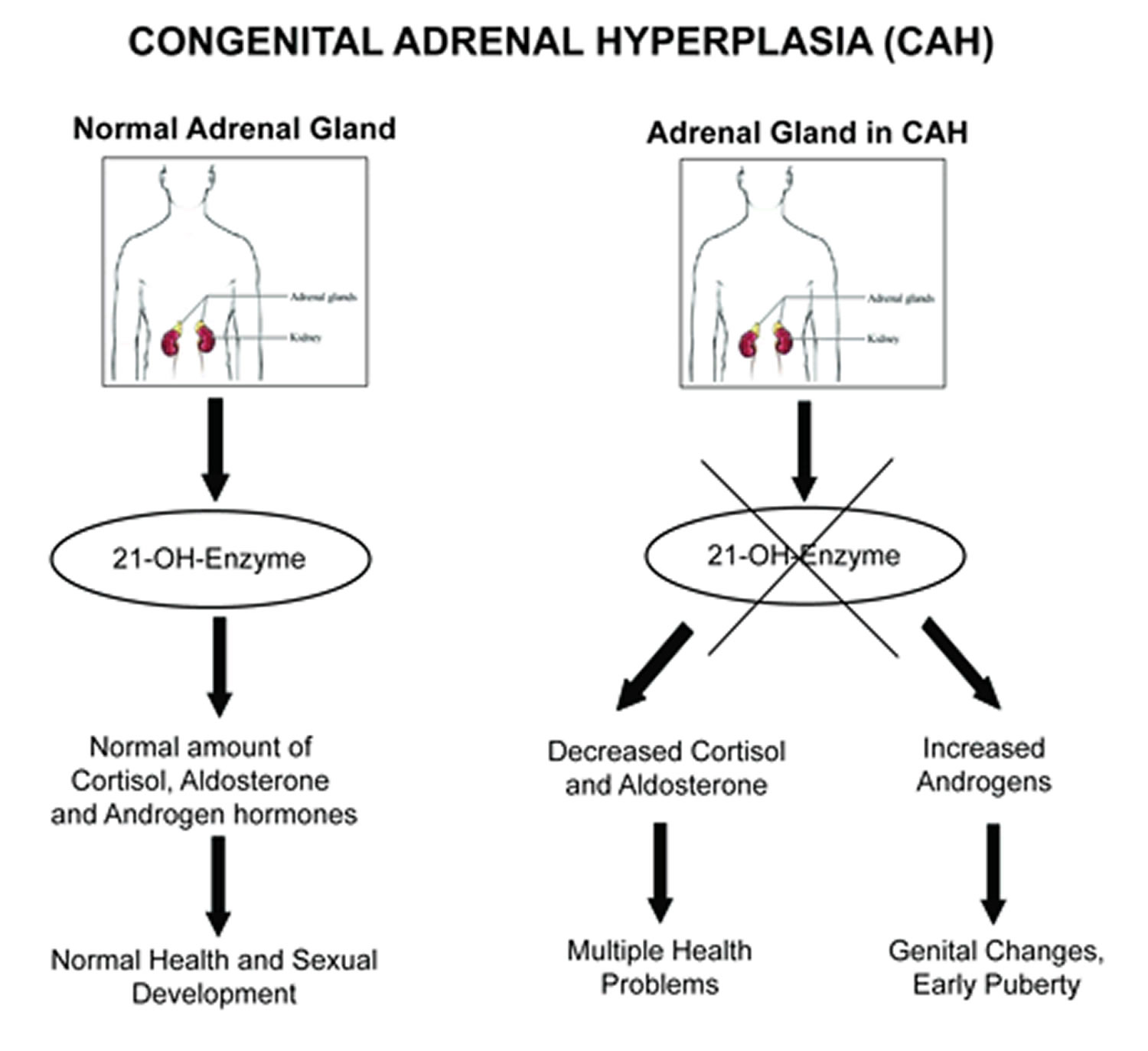
If asymptomatic no treatment is required. Treatment for 21-hydroxylase deficiency depends on the severity of symptoms and the form of the condition. Cortisol and aldosterone synthesis are impaired in the classic forms adrenal insufficiency and salt-wasting crisis.
Treatment for 21-hydroxylase defiency can begin in utero in order to prevent over virilization of XX fetuses. Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Rapidacceleratedgrowth is stimulated and sexual precocity develops in both male and female patients who are not treated after the neonatal stage.
Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of individuals with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency have been published Speiser et al 2010. The Guidelines for Treatment of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency Found in Neonatal Mass Screening 1999 revision published in 1999 were revised to include 21-OHD patients with very mild or no clinical symptoms. Mineralocorticoid replacement is not needed.
If symptomatic corticosteroid treatment is similar to classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency but lower doses are often effective. Cortisol and aldosterone synthesis are impaired in the classic forms adrenal insufficiency and salt-wasting crisis. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the CYP21A2 gene.
Infants identified at birth with 21-hydroxylase deficiency are treated with hormones and steroids to prevent a salt-wasting crisis. Females affected are virilised at birth and are at risk for genital ambiguity.
21 Hydroxylase Deficiency Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis

Adrenal Steroidogenesis In 21 Hydroxylase Deficiency Congenital Adrenal Download Scientific Diagram
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia

Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused By 21 Hydroxylase Deficiency Pediatrics Merck Manuals Professional Edition

Adrenal Gland Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Adrenal Insufficiency Dr Amnon Zung Pediatric Endocrinology Unit Kaplan Medical Center Ppt Download



0 comments:
Post a Comment