The most effective drug for treating malaria is artemisinin which is usually given as part of a combination therapy a cocktail of drugs intended to treat the disease while reducing the risk of the emergence of parasites resistant to one particular drug. For the second and third trimester of pregnancy results from several trials have confirmed that artemisinin-based combination treatments are safe and efficacious although tolerability and efficacy might vary by treatment.

Word Malaria Day 2021 How To Treat Malaria During Pregnancy
The World Health Organization WHO now recommends that all women in the second or third trimester of pregnancy who have uncomplicated P.

How to treat malaria during first trimester. Treatment appeared to be safe. The present study aims at assessing the maternal and birth outcomes in pregnant women who were inadvertently exposed to AL during first. Treatment for uncomplicated malaria in pregnancy First trimester.
For P falciparum malaria infections during the first trimester WHO recommends quinine with clindamycin for 7 days or quinine alone if clindamycin is not available. The 2010 WHO guidelines recommend using either quinine or artesunate for the treatment of severe malaria in first trimester pregnancies Current data suggest that WHO treatment guidelines should be changed to recommend artesunate as the preferred treatment option for severe malaria in pregnancy during all three trimesters. Treat pregnant women with uncomplicated P.
Severe malaria should be treated with intravenous IV antimalarial medications. For the treatment of malaria during the first trimester international guidelines are being reviewed by WHO. The national guidelines and PMI reports of several representative SSA and GMS countries recommend quinine monotherapy for 7 days as the preferred regimen administered under full supervision for treating uncomplicated malaria during first trimester Table 2.
Vivax is able to re-emerge from the liver stage which cannot be treated in pregnancy. Artesunate for Injection TM was approved by the FDA and is commercially available in the United States. Falciparum malaria should be treated.
During early pregnancy treatment options are limited especially in regions with drug. Treatment of clinical uncomplicated malaria episodes in women in the first trimester of pregnancy should be updated as follows. WHO recommends Intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy with sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine IPTp-SP in all areas with moderate to high malaria transmission in Africa for all pregnant women at each scheduled antenatal care visit except during the first trimester.
WHO recommends a combination of quinine and clindamycin in the case of uncomplicated pregnancy malaria detected during the first trimester. This is a precaution even though theres no evidence to suggest mefloquine is harmful to an unborn baby. Malaria during pregnancy has adverse effects including maternal mortality miscarriage and low birthweight.
In the second and third trimesters artesunate plus clindamycin can be administered or the artemisinin-based combination therapy ACT commonly used in that region although some of. Medications that can be used for the treatment of malaria in pregnancy include chloroquine quinine atovaquone-proguanil clindamycin mefloquine avoid in first trimester sulfadoxine. This is because animal studies have indicated that the drugs can be toxic to embryos.
Despite its reactogenicity profile and several reports of resistant strains of P falciparum17 18 quinine remains the only recommended drug for treating both uncomplicated and complicated P falciparum malaria during first trimester of pregnancy5 11. For P falciparum malaria infections during the first trimester WHO recommends quinine with clindamycin for 7 days or quinine alone if clindamycin is not available and in situations of failure or unavailability an artemisinin-based combination therapy ACT or oral artesunate with clindamycin for 7 days. Artemisinin-based combination therapy ACT is recommended by the World Health Organization as the treatment for all malaria caused by the P.
Currently first-line treatment options for uncomplicated malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum many strains of which are resistant to chloroquine is quinine plus clindamycin doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnant women. Falciparum malaria with either the first-line ACT for 3 days or quinine and clindamycin for 7 days Artemether-lumefantrine AL should be the preferred ACT because most. Uncomplicated malaria in first trimester.
Falciparum species of malaria parasite except in the first trimester of pregnancy. The CDC now recommends the use of artemether-lumefantrine as an additional treatment option for uncomplicated malaria in pregnant women in the United States during the second and third trimester of. Mefloquine not usually prescribed during the first trimester of pregnancy or if pregnancy is a possibility during the first 3 months after preventative antimalarial medication is stopped.
IV artesunate is the first-line drug for treatment of severe malaria in the United States. Symptomatic and asymptomatic malaria infections during the first trimester of pregnancy were associated with miscarriage.

Treatment Of Uncomplicated Malaria Among Women Of Reproductive Age Maternal Child Survival Program
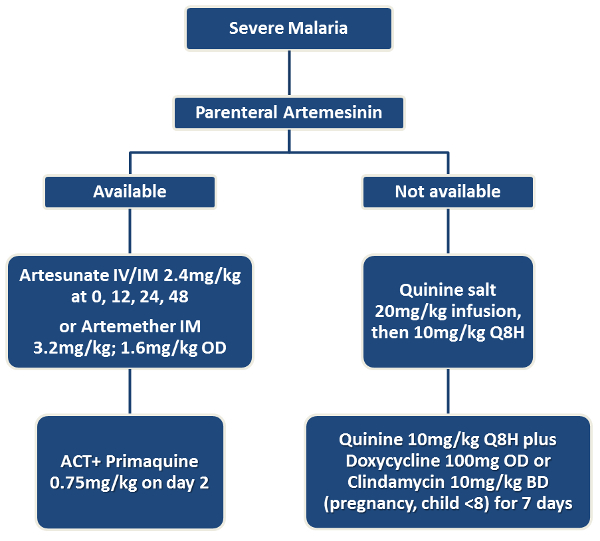
Treatment Of Malaria Malaria Site

Pdf Treatment And Prevention Of Malaria In Pregnancy And Newborn

Treatment Of Malaria Malaria Site
Artemisinins Should Replace Quinine For First Trimester Malaria Treatment Says New Study Moru Tropical Health Network

Malaria In Pregnancy Access To Effective Interventions In Africa Yartey 2006 International Journal Of Gynecology Amp Obstetrics Wiley Online Library

Pdf Treatment And Prevention Of Malaria In Pregnancy And Newborn

Lesson 7 Malaria In Pregnancy Wikieducator

Pdf Treatment And Prevention Of Malaria In Pregnancy And Newborn

0 comments:
Post a Comment