Separate animals that are aborting from the rest of the herd. With heart valve or blood vessel disease With weakened immune systems Who were pregnant when they first had Q fever.
Farm animals and pets are the main reservoirs of infection and transmission to human beings is mainly accomplished through inhalation of.

Q fever treatment in animals. Burnetii bacterium is highly infectious and only a tiny amount is needed to cause disease. Handling of infected tissue poses a threat to laboratory personnel. 4 good manure management.
One is prophylactically and the other is upon recognition of symptoms. More severe or chronic forms of Q fever can be treated with antibiotics. Patients usually recover promptly when treatment is started without delay.
Burnetii bacteria are found in the birth products ie. Q fever is a widespread disease caused by the bacteria Coxiella burnetii which is able to infect mammals birds reptiles and arthropods. Consult your health care provider if you have symptoms that might indicate Q fever.
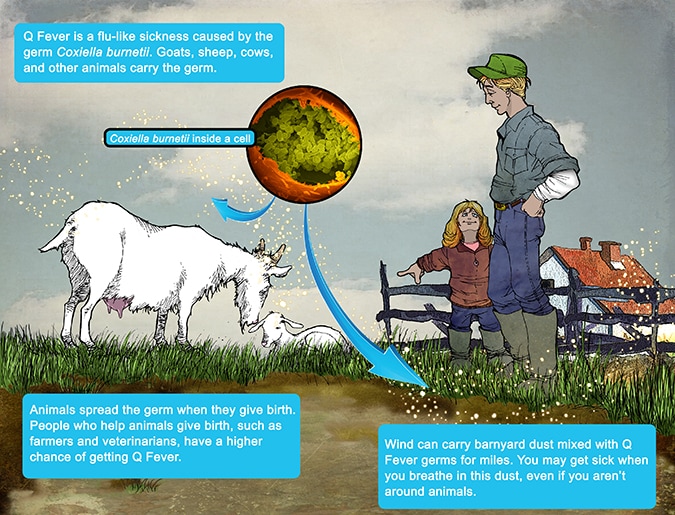
Q fever bacterium primarily infects farm animals such as cattle sheep and goats. People can get infected by breathing in dust that has been contaminated by infected animal feces urine milk and birth products. Any contaminated clothing taken home should be bagged and washed separately only by those immune to Q fever.
Medical facilities using ruminants in research should attempt to purchase animals from flocks free of coxiellosis or use male animals when possible. Prophylactically the antibiotic can be added to the drinking water of dogs and farm animals that are. A very small number of people with Q fever less than 1 out of 20 develop a more severe illness called chronic Q fever.
Cover all open wounds with waterproof bandaging. PPE is not a substitute for Q fever vaccination. Fever can be treated with certain antibiotics.
It is also a zoonosis a disease of animals. Infections caused by Coxiella burnetii commonly referred to as coxiellosis when occurring in animals and Query fever when occurring in humans are an important cause of abortions decreased reproductive efficiency and subclinical infections in ruminants. Dispose of all birth remains properly and feed your dog pasteurized products.
In most cases persons with acute Q fever will recover without antibiotics. Q fever is an worldwide endemic affecting cats and dogs of any age gender or breed and as a zoonotic disease it is transmissible to humans. This bacteria naturally infects some animals such as goats sheep and cattle.
Both methods utilize the antibiotic Tetracycline. Wash the soiled clothing separately from personal clothes and preferably at the animal facility. Placenta amniotic fluid urine feces and milk of infected animals.
There are two methods of treating Q Fever in dogs. 3 removal of risk material from birthing areas birthing productsfluids contaminated bedding manure. And 6 restriction of moving peri-parturient animals.
Care must be taken when dealing with bodily fluids organs andor tissue material of any animal particularly farm animals. Q fever has been seen in personnel and human patients in medical institutions where latently infected sheep were used for research. Q fever is a disease caused by the bacteria Coxiella burnetii.
2 segregated kiddinglambing areas. It causes a mild disease in ruminants but can cause abortions and still births in cattle sheep and goats. Although it may not be practical or possible to eliminate the risk of Q fever in a typical farm setting the risk for spread can be decreased by 1 proper sanitation good hygiene especially when working with parturient animals.
Ill individuals who work with sheep and goats must communicate clearly with their health care provider about their previous exposure to these animals and their facilities bedding or manure. Chronic Q fever is more likely to occur in people. In humans antibiotics may be used to treat severe or chronic cases.
Symptoms may not appear until months or years after exposure. There are currently no labeled therapies for livestock infected with Q Fever in the US. The organism also represents an important zoonotic concern associated with its ability to aerosolize easily and its low infectious dose.
Those at risk for Q fever can prevent the disease by disinfecting contaminated areas and washing their hands thoroughly. It is recommended to work with your veterinarian if you suspect abortions due to Q fever. Doxycyline is the treatment of choice for Q fever and is most effective if administered within the first 3 days of infection.
However it has been reported in a wide variety of animals including domesticated animals such as dogs and cats. If needed the antibiotic tetracycline doxycycline is often used to treat acute Q fever. 5 control of ticks on livestock.
Q fever is treated with antibiotics such as doxycycline quinolones and combined doxycycline and quinolones. Your veterinarian can diagnose and provide treatment recommendations for coxiellosis and may prescribe medications to reduce the spread of the bacteria. This crucial step communicating about potential exposure very important in helping your health care.
What is the prognosis for Q Fever. Q fever is a zoonotic disease caused by the ubiquitous pathogen Coxiella burnetii responsible for acute and chronic clinical manifestations. Chronic Q fever can result in infection of heart valves called endocarditis.

Q Fever Fact Sheet Q Fever Cdc

Q Fever Coxiella Burnetii Dr Hani Masaadeh Md Phd Ppt Download
Https Education Qld Gov Au Initiativesstrategies Documents Factsheet Q Fever Pdf

Source And Transmission Of Q Fever Download Scientific Diagram

Q Fever Oie World Organisation For Animal Health
/overview-of-q-fever-4177937_color1-5c454c4bc9e77c000153bca5.png)
Q Fever Symptoms Causes And Treatment

The Importance Of Ticks In Q Fever Transmission What Has And Has Not Been Demonstrated Trends In Parasitology

Source And Transmission Of Q Fever Download Scientific Diagram

0 comments:
Post a Comment