PNGase F was used for deglycosylation of P-glycoprotein in a study to investigate the dual impact of statins on p-glycoprotein and its effect on doxorubicin cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma cells. Depending on the application solutions containing higher or lower enzyme activity may be prepared.
Rapid Pngase F By Sds Page Protocol P0710 Neb
P0705L was used to remove the N-glycan by incubating 1 mg of each antibody with 275 units of PNGase F at 37C for 24 hours.
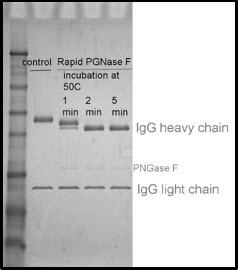
Pngase f treatment. PNGase F is inhibited by SDS therefore it is essential to have NP-40 in the reaction mixture under denaturing conditions. ESI-TOF analysis of an antibody before and after treatment with Rapid PNGase F Specificity Rapid PNGase F cleaves all complex hybrid and high-mannose type glycans from antibodies and related proteins 1. PNGase F digestion.
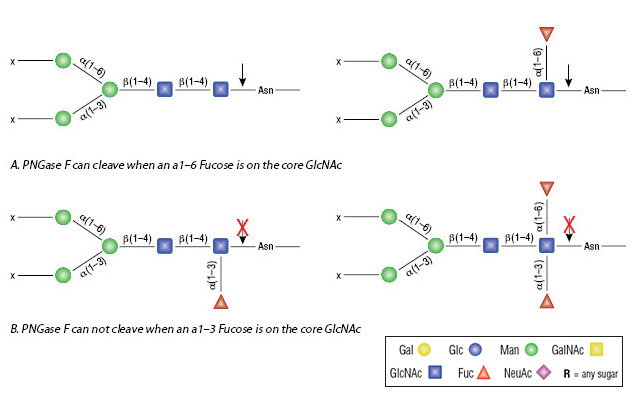
PNGase F will not remove oligosaccharides containing Alpha-13-linked core fucose commonly found on plant glycoproteins. PNGase F New England Biolabs cat. Core α1-3 fucosylation found in immunoglobulins expressed in plant or insect cells is resistant to both PNGase F and Rapid PNGase F.
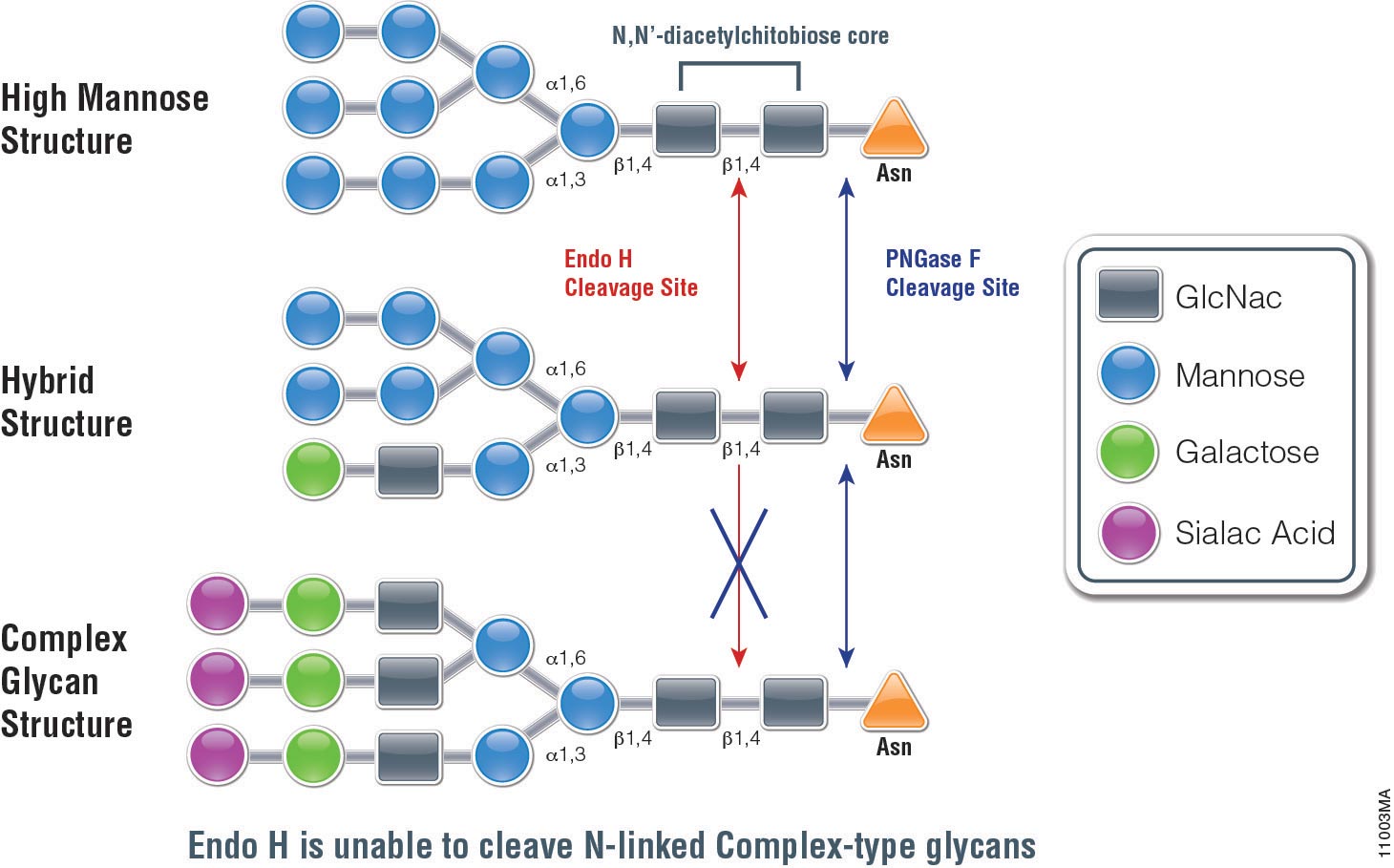
High mannose hybrid bi- tri- and tetra-antennary. You will choose this enzyme if your goal is to remove all N -linked carbohydrates without regard to type. Add 1 µl PNGase F mix gently.
Denaturation of proteases. Failure to include NP-40 into the denaturing protocol will result in loss of enzymatic activity. Glycans released from the intact IgG1 by PNGase F treatment were enriched using the 96-well MassPREP HILIC µElution plate accord-ing to the Waters Care and Use Instructions and a published paper by Yu and colleagues2.
N A µElution plate well was washed with 200 µL of Milli-Q water. Denatured substrates provide PNGase F with efficient access to the oligosaccharide-protein linkage. PNGase F is the most effective enzymatic method for removing almost all N -linked oligosaccharides from glycoproteins.
After PNGase F treatment the S1 and S2 subunits were reduced by 30 kDa and 20 kDa in weight respectively Figure 2C. PNGase F Promega treatment was used as a positive control which contained 2 μl PNGase F 1 mU which is defined by the manufacturer as the amount of enzyme required to catalyse the release of N -glycans from 1 μmol of denatured RNAse B per minute at pH 75 and 37C enzyme solution 3 μl of glycopeptide substrate 10 pmolμl 75 μl 500 mM phosphate buffer pH 75 15 μl 10 Triton X-100. Prepare a 500 unitsml solution by adding 100 ml of high purity water to a vial of 50 units.
Before opening the vial containing PNGase F centrifuge the vial briefly to ensure the lyophilized material is at the bottom of the tube. Use of the endoglycosidic enzyme PNGase F N-Glycosidase F is the most effective method of removing nearly all N-linked oligosaccharides from glycoproteins. You would choose this enzyme to.
Use of PNGase Fast denaturing buffer and enzyme yielded results similar to a conventional 20-hour protocol with overnight digest while reducing workflow time to about 1 hour with a 15 minute digest. Endo H removes only high mannose and some hybrid types of N -linked carbohydrates. Failure to include NP-40 into the denaturing protocol will result in loss of enzymatic activity.
Incubate reaction at 37C for 1 hour. In the next stage PNGase F treatment is employed for deglycosylation of glycoproteins resulting in conversion of Asn. Analyze by method of choice.
PNGase F is inhibited by SDS therefore it is essential to have NP-40 in the reaction mixture under denaturing conditions. PNGase F cleaves all asparagine-linked complex hybrid or high mannose oligosaccharides unless the core contains an α 13-fucose. PNGase F is the most effective enzymatic method for removing almost all N -linked oligosaccharides from glycoproteins.
PNGase F digestion deaminates the aspargine residue to aspartic acid and leaves the oligosaccharide intact keeping it suitable for further analysis. PNGase F digestion deaminates the aspargine residue to aspartic acid and leaves both the protein and the oligosaccharide intact keeping them suitable for further analysis 1. To establish a standard procedure to evaluate N-glycan release from whole human serum glycoproteins by peptide-N-glycosidase F PNGase F treatment we determined the efficiencies of major N-glycan liberation from serum glycoproteins in the presence of reducing agents surfactants protease treatment or combinations of pretreatments prior to.
Briefly the method used to extract glycans was as follows. Substrate reduction prior to PNGase Fast treatment is optional but required for complete deglycosylation of some samples. One unit of PNGase F will catalyze the deglycosylation of 1 nanomole of denatured Ribonuclease B RNase B in one minute at 37C.
Incubate reaction at 37C for 1 hour. PNGase F is often most effective at deglycosylating protein substrates that are first denatured. PNGase F removes almost all types of N -linked Asn-linked glycosylation.
Typically with detergents and reducing agents. After digestion sulfopropyl-sepharose cation exchange chromatography was used for purification. This results in an enzyme solution containing 5 mM potassium phosphate buffer pH 75.
Add 1 µl PNGase F mix gently. The bands corresponding to S1 and S2 before PNGase F treatment were analyzed by MS to reveal the glycan compositions.

Strategies For Deglycosylating N Linked Glycans
Endo H Application Monitoring Protein Trafficking Promega Connections

Enzymatic N Deglycosylation Using Pngase F Western Blot Revealed The Download Scientific Diagram

Deglycosylation Assay Of Blv Gp51 Using Pngase F And Endo H A Download Scientific Diagram

Proteins Of Purified Yhv Particles Digested With Pngase F Were Resolved Download Scientific Diagram

Deglycosylation Of Hgsnat By Endoglycosidase H Pngase F And Download Scientific Diagram

Recombinant Pngase F For Glycoprotein Analysis

Deglycosylation And Biotinylation Of Trpm5 A Treatment With Pngase F Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments:
Post a Comment