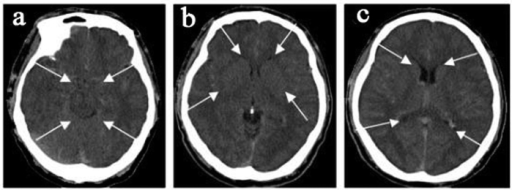
Edema of the brain is the accumulation of free fluid in the brain tissue intercellular space. Common causes include a traumatic brain injury stroke tumor or infection.
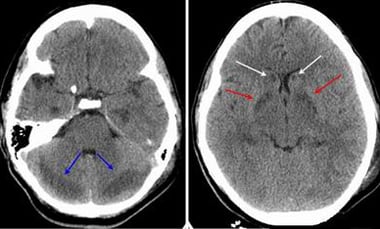
Primary Causes Of Cerebral Edema Brain Swelling
If it drops your brain.
How to treat edema in brain. Sleep with a. Brain swelling is an urgent clinical problem that frequently accompanies ischemic stroke brain hemorrhage and traumatic brain injury and it increases morbidity and mortality associated with them. For edema caused by lifestyle or temporary conditions there are several remedies to provide relief.
This surgery could mean removing part of the skull or removing the source of. It can result from overuse or infection. In this article learn about the symptoms of cerebral edema as well as how doctors diagnose and treat the condition.
Elevate your legs or arms above the level of your heart a few times a day. Oxygen Therapy Oxygen therapy helps ensure that your blood has enough oxygen in it which can help control swelling. In more severe cases of cerebral edema you may need surgery to relieve ICP.
Intravenous Fluids IVs help prevent your blood pressure from dropping too low. The diverse pathogenetic factors leading to edema-swelling of the brain can be reduced to two main. Here are some of the common treatments for brain swelling.
Swelling -- also called edema -- is the bodys response to many types of injury. How is brain edema treated. When possible corticosteroids should be used in a low dose eg 4 mg dexamethasone daily to avoid serious side effects such as.
If pressure is limiting or preventing adequate supply medical intervention may be necessary. The aim of the treatment for cerebral edema is to decrease the swelling around the brain and reduce the pressure being put on the brain and ensure proper blood supply reaches the brain so that the cells do not start dying due to oxygen depletion. Treatment approaches can include osmotherapy using mannitol diuretics to decrease fluid volume corticosteroids to suppress the immune system hypertonic saline and surgical decompression to allow the brain tissue room to swell without compressive injury.
With increasing vascular permeability interstitial edema develops with parenchymal damage - brain swelling. Currently available to control brain swelling include osmotic agents with emphasis on mannitol and hypertonic saline solutions corticosteroids hyperventilation sedation propofol barbiturates neuromuscular paralysis hypothermia and surgical interventions. Usually swelling happens quickly and is simple to treat with some.
Corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment of brain edema. Medications Some medications can help treat brain swelling by decreasing the likelihood of clot formation. Osmotherapy is a treatment meant to draw water out of the brain.
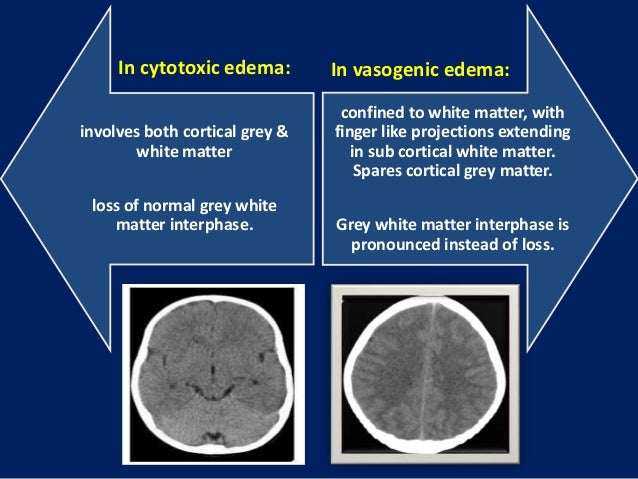
It occurs due to failure of membrane transporters and the blood-brain barrier BBB resulting in combination of cytotoxic ionic and vasogenic edema. This is done using osmotic agents such as mannitol high-salt saline glycerol and drugs such as.
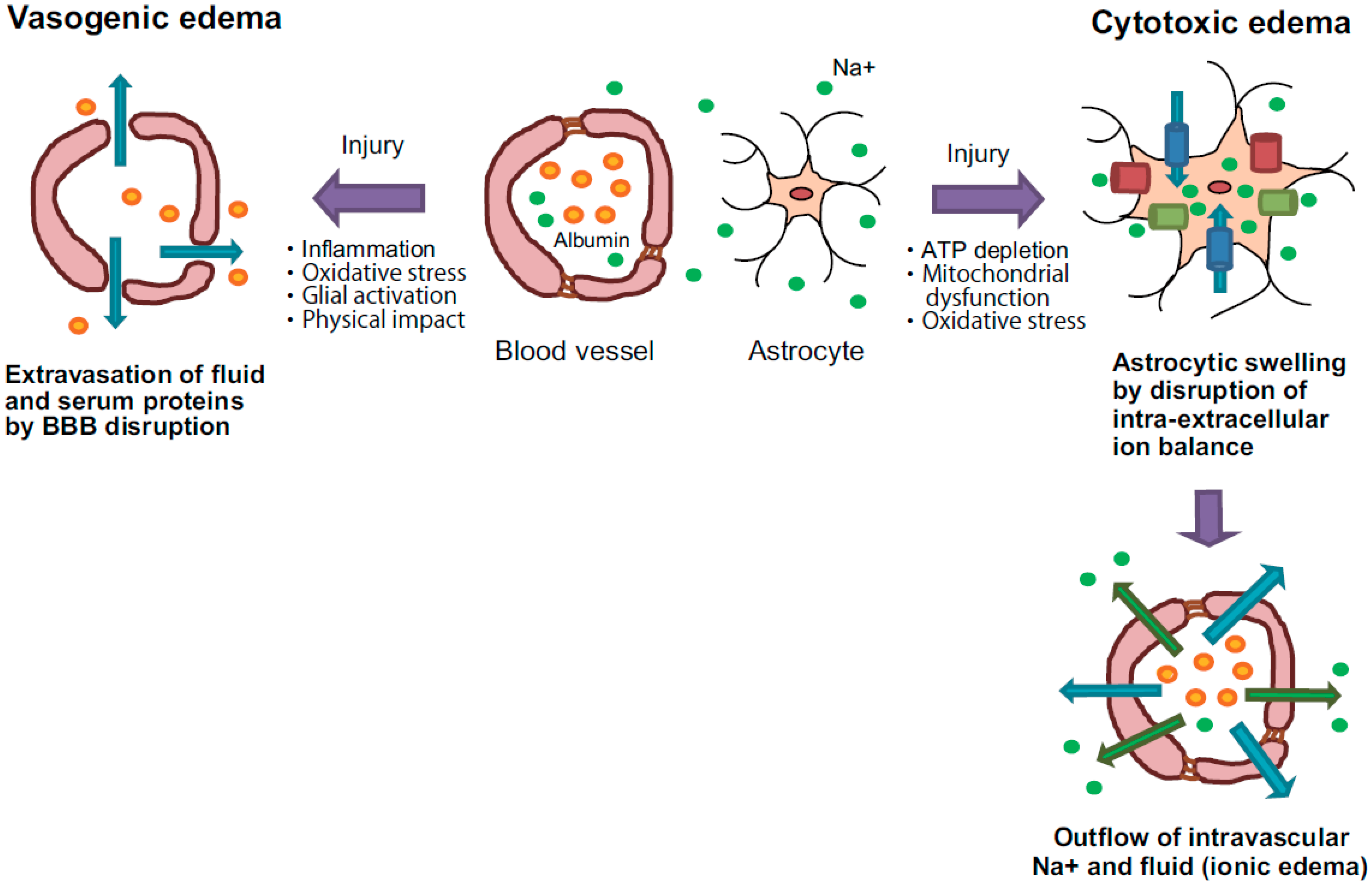
Ijms Free Full Text Pathogenesis Of Brain Edema And Investigation Into Anti Edema Drugs Html

Cerebral Edema Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention
Cerebral Edema Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention

Cerebral Edema Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention

Cerebral Edema Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention

Cerebral Edema Causes Symptoms Treatment Prognosis
Cerebral Edema Causes And Treatment Guidelines

0 comments:
Post a Comment