Glucocorticoids have shown potential benefit in cerebral edema secondary to vasogenic edema but have limited utility in other forms of edema and should be avoided altogether in the face of trauma. The latter type of edema ie vasogenic edema and the role of other types in brain tumors is discussed.
For maintenance therapy they recommend that 2 mg twice or three times daily may be effective.

How to treat vasogenic edema. Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Vasogenic Pericontusional Edema. Treatment depends on the edemas severity and the timeliness of medical attention. Appendage edema is often treated by bandaging the area to relieve pressure on the skin and decrease venous pressure.
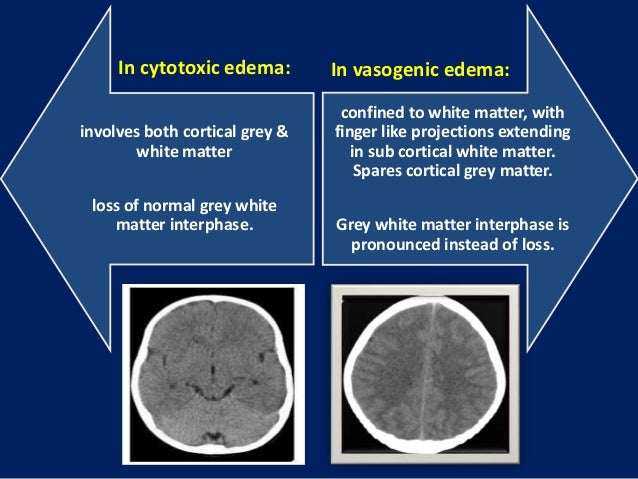
Anticonvulsant prophylaxis and steroid use in adults with metastatic brain tumors. Fluid leaving the capillaries enlarges the extracellular space predominantly in the white matter. It is an extracellular edema which mainly affects the white matter via leakage of fluid from capillaries.
IV fluids may be administered to treat a vasogenic edema. When possible corticosteroids should be used in a low dose eg 4 mg dexamethasone daily to avoid serious side effects such as. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the US.
Cytotoxic cerebral edema where the BBB is intact. Cytotoxic cerebral edema where the blood-brain barrier remains intact. The accumulation of fluid within the lungs is a serious complication of cardiac failure pneumonia and other disorders.
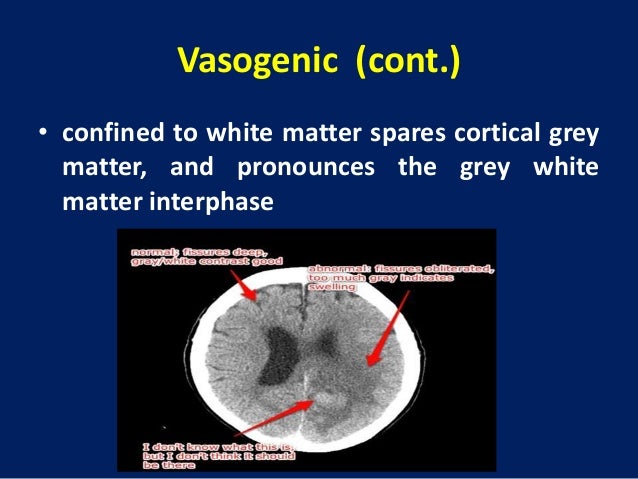
The brain needs an uninterrupted flow of oxygen to function. Various treatment options include oxygen therapy where oxygen is provided. Vasogenic edema is the endpoint of many acute neurological disorders as described in the preceding section and is characterized by BBB breakdown to plasma proteins.
The vasogenic edema that surrounds many brain tumors contributes significantly to morbidity. Hernia-tions and vascular lesions are particularly important because they create serious clinical situations and death can ensue. The pathogenesis of peritumoral vasogenic edema and the use of glucocorticoids are reviewed here.
The primary treatment objective is maintaining adequate blood and oxygen flow to the brain while relieving any swelling and treating the underlying cause of the edema. It is most frequently seen around brain tumors both. Brain edema in brain tumors is the result of leakage of plasma into the parenchyma through dysfunctional cerebral capillaries.
Progressive brain swelling due to the edema leads to cerebral herniations and death hence the. More severe cases may require a surgical procedure that diverts the blood flow to healthy veins. Increased ICP can reduce brain blood flow and decrease the oxygen your brain receives.
Chang SM Messersmith H Ahluwalia M et al. It is an extracellular edema which mainly affects the white matter via leakage of fluid from capillaries. A wide range of doses of dexamethasone have been used for vasogenic edema.
This edema results from disruption of the blood-brain barrier allowing protein-rich fluid to accumulate in the extracellular space. The main analysis will be on an intention-to-treat basis. Vasogenic edema is characterized by dysfunction of the blood-brain barrier allowing an abnormal passage of proteins electrolytes and water into the extracellular compartments.
Corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment of brain edema. Edema is a frequently encountered problem in clinical practice but effective treatment of this condition is a relatively recent development1 The etiology of edema. Intracranial expanding mass lesions such as neoplasms abscesses granulomas and hematomas induce a vasogenic edema which if not resolved leads to herniations vascular lesions and bony erosions Table 27.
DEXCON-TBI The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment of brain edema. Osmotic and hydrostatic gradients will also cause interstitial edema.
Vasogenic cerebral edema refers to a type of cerebral edema in which the blood brain barrier BBB is disrupted cf. Summary of SNO and ASCO endorsement of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons guidelines. Vasogenic cerebral edema refers to a type of cerebral edema in which the blood brain barrier BBB is disrupted cf.
Use of dexamethasone in treatment of cerebral edema associated with brain tumors. Avoidance of hypotonic fluids is a strong recommendation in instances of cerebral edema as they can worsen cerebral edema and cause elevations in ICP. The FDA-approved labeling indicates an initial dose of 10 mg IV followed by 4 mg every six hours IM.
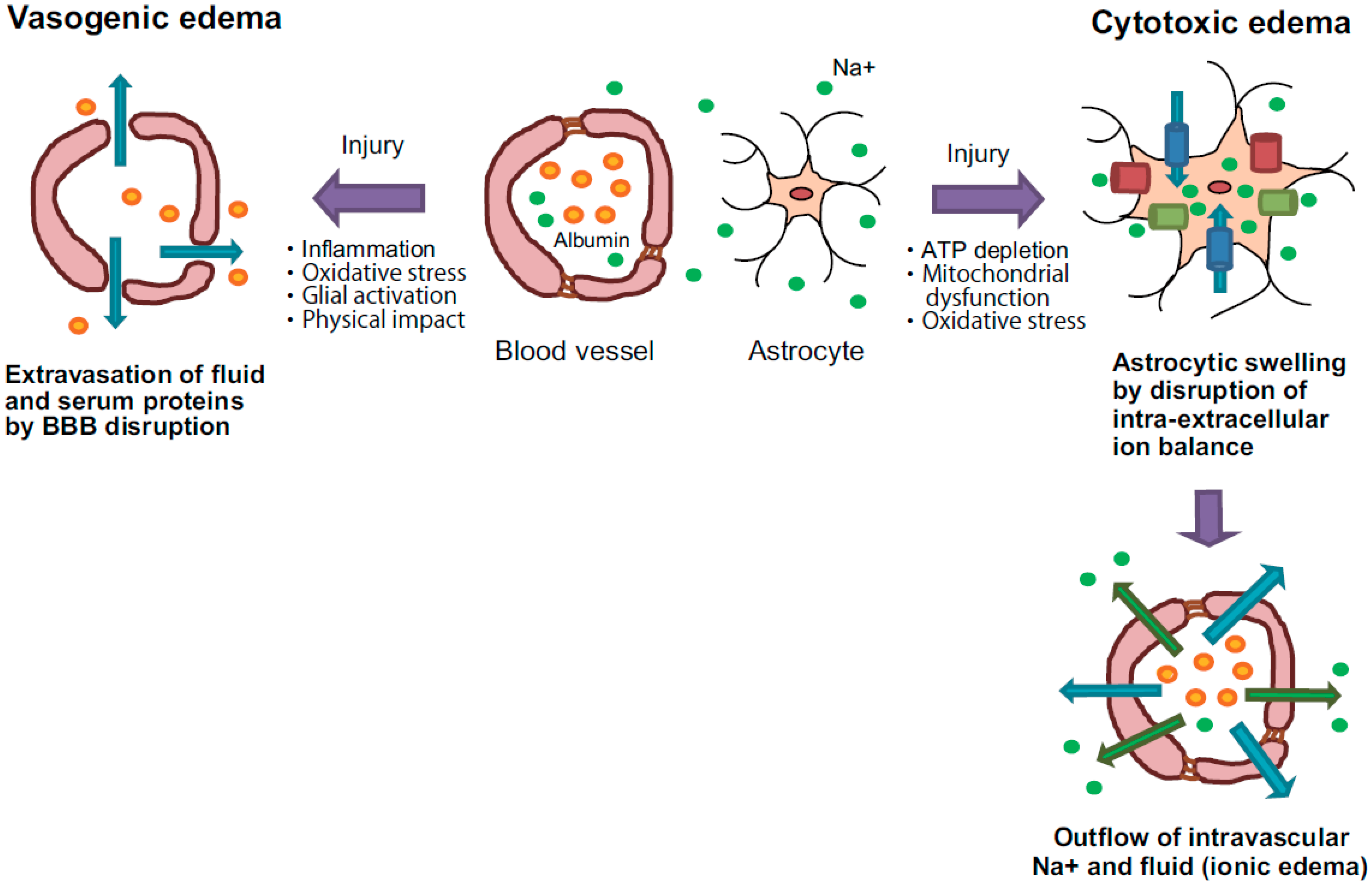
Ijms Free Full Text Pathogenesis Of Brain Edema And Investigation Into Anti Edema Drugs Html

Ijms Free Full Text Pathogenesis Of Brain Edema And Investigation Into Anti Edema Drugs Html

Biphasic Function Of Aqp4 In Cytotoxic And Vasogenic Edema Download Table
Cerebral Edema Causes And Treatment Guidelines

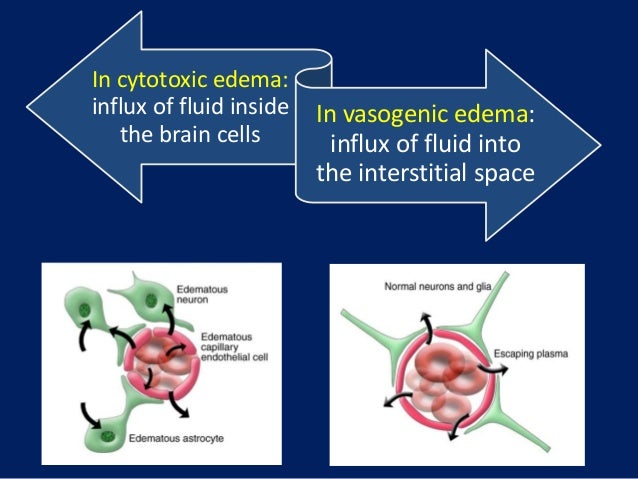
Schematic Demonstrating Cytotoxic And Vasogenic Cerebral Edema Download Scientific Diagram
Vasogenic Cerebral Edema Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

0 comments:
Post a Comment