M4 is an extremely versatile high-speed steel with its extremely high carbon and vanadium contents for exceptional abrasion-resistance. Such a heat treatment results in an austenite grain size of between.
Heat Treatment Of Steels The Processes
When metal M is treated with N a O H a white gelatinous precipitate X is obtained which is soluble in excess of N a O H.

M treated steel. The purpose of this treatment is increasing the surface energy level of a particular metal surface so that it can easily adhere to the printing or coating that is about take place. The Heat Treatment of PM Tool Steels In Materials Science Forum vol. Heat treating or heat treatment is a group of industrial thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a materialThe most common application is metallurgicalHeat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials such as glassHeat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling normally to extreme temperatures.
E8 for wrought steels machined from sintered impact blanks. The test method and data may be compared directly with that for wrought steels. ASTMs steel standards are instrumental in classifying evaluating and specifying the material chemical mechanical and metallurgical properties of the different types of steels which are primarily used in the production of mechanical components industrial parts and construction elements as well as other accessories related to them.
M-Steel machining compared to conventional steel. Trans Tech Publications Ltd 1992. Tempering is a process of heat treating which is used to increase the toughness of iron-based alloysTempering is usually performed after hardening to reduce some of the excess hardness and is done by heating the metal to some temperature below the critical point for a certain period of time then allowing it to cool in still air.
A rule of thumb is. M-Steel treatment can be applied to any steel grade and any as-delivered condition. The harder the machined steel the more benefit you get with the M-steel.
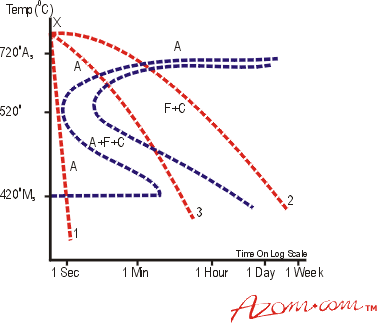
In very simple words I am going to explain the heat treatment process consists of a succession of heating and cooling cycles applied to a metal or alloy in order to obtain the desired properties such as hardness ductility tensile strength toughness grain size etc. The exact temperature determines the amount of hardness. The treatment of metal is a process in which parts or components made out of metal are treated before any actual coating takes place.
This study was conducted in order to improve the mechanical properties of mild steel materials used as bolts and studs in coupling agricultural machinery following their frequent failure in service. 8Cr steel and 10Cr steel offer improved machinability for better processing that reduces the volume of hard carbides within steel but are inferior to SKD11 in terms of wear resistance and galling. This test piece is located within the testing grips by machined threads.
26 rows Variant 5081 is a M-treated variant wich is offered under the name Imatra 4M. Compound X when heated strongly gives an oxide which is used in chromatography as an adsorbent. It is well suited for premium cutting tools of all types particularly those used for machining abrasive alloys castings and heat-treated materials.
Use of an Iron-Base Alloy in the Manufacture of Sintered Parts With a High Corrosion Resistance a High Wear Resistance as Well as a High Toughness and Compression. It almost eliminated the problems of gripping under load and premature failure observed with heat treated high strength PM steels. 4 Kulmburg A J.
MMD is a privately-owned steel manufacturing company committed to sustainable safe and self-sufficient steel production in Africa. Castle Metals uses a state-of-the-art in-house heat treating facility to deliver custom properties to carbon and alloy steel products as well as some stainless steels. As the leading manufacturer of TMT rebars high-quality thermo mechanically-treated steel reinforcement bars and merchant bars MMDs products are used to construct residential commercial industrial and civil structures.
Then metal M is. Although the steel becomes fully austenitic at temperatures in excess of about 900 C this is under equilibrium conditions but austenitisation at 1040 C for 20 min is found in practice to completely dissolve the cementite in 52100 steels containing as much as 11 wt carbon. Surface treatment properties are based on adherence between the coating layer and steel after surface treatment.
Heat treatment at 900 0 C for four hours was done and six specimens of each were then quenched with different media used as the major source of strength enhancement. This means that hard quench and tempered M-steel 300-400 HB. Fundamentals of the Heat Treating of Steel 11 Steel however is by far the most widely used alloy and for averygood reason.
Induction heating induction hardening tempered steel and general heat treatment of steel are several things we hear as customers look to learn more about how to harden. Among layman the reason for steels dominance is usually con-sidered to be the abundance of iron ore iron is the principal ingredient in all steels andor the ease by which it can be refined from ore.

How To Harden Steel 10 Steps With Pictures Wikihow

Knife Material Selection Aceco Industrial Knives

Revealing The Microstructure Of Tool Steels

En8 Carbon Steel 080m40 Bs 970 Specification Otai Special Steel

How To Harden Steel 10 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
.jpg)
Aisi 4140 Alloy Steel Uns G41400
.jpg)
Aisi 4130 Alloy Steel Uns G41300
.jpg)
Aisi 1018 Mild Low Carbon Steel

0 comments:
Post a Comment