Pylori-positive patients including children and elderly subjects. The draft recommendations developed based on the meta-analysis were finalized after an expert consensus on three recommendations regarding the indication for treatment and eight recommendations for the treatment.

Reconciliation Of Recent Helicobacter Pylori Treatment Guidelines In A Time Of Increasing Resistance To Antibiotics Gastroenterology
Due to the increase in the prevalence of H.

Treatment h pylori guidelines. Pylori eradication can effectively prevent H. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection is important for the management of gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcer and gastric cancer. However a limited selection of antibiotics.
Antibacterial activity towards H. Pylori infection and all treatments should be given for 14 days. Some antibiotics including clarithromycin and amoxicillin also require intragastric acid suppression for maximum efficacy and sustained activity.
Pylori is shown by many antibiotics amoxicillin macrolides tetracyclines and some other chemotherapeutic agents nitroimidazoles and bismuth. Screening or testing for H. As antibiotic susceptibility data are not usually available empiric first-line therapies should be based on some knowledge of patients previous antibiotic exposure and history of penicillin.
PPIs are recommended because through increase of pH in stomach they create conditions to act for antibiotics. H pylori is most susceptible to antibiotics when the intragastric pH is consistently between 6 and 8 because this is the optimal pH range for H pylori replication. Pylori especially in some areas where the local resistance to this antibiotic is higher than 20.
Pylori infection is to succeed on the first attempt thereby avoiding re-treatment and reducing cost anxiety and the further promotion of resistant strains. Pylori infection is associated with various gastric and extra-gastric diseasesImportantly this infection is the strongest known risk factor for gastric cancer GC. The number of treatment options for H.
All treatment guidelines agree that the best approach to the treatment of H. Pylori infection has substantially increased since publication of the 2007 ACG guideline Tables 2 and 4. All of the modern treatment regimens including concomitant therapy hybrid therapy and levofloxacin-containing regimens which have been found to be most effective in international trials have not been evaluated in North America.
Helicobacter pylori H. Pylori were updated according to evidence-based medicine from a metaanalysis conducted on a target group receiving the latest level of eradication therapy. Current international guidelines recommend a standard triple therapy as first-line therapy including a proton pump inhibitor and a combination of amoxicillin and clarithromycin.
A lthough the prevalence of H pylori is decreasing in some parts of the world the infection remains pre-. Serologic H pylori test result ie a breath- stool- or gastroscopy-based test at least 4 weeks after 1 or more completed courses of a current guideline-recommended first-line H pylori eradication therapy and off of any medi-cations such as proton-pump inhibitors PPIs that might impact the test sensitivity4 Refractory H pylori infection. Pylori infection-associated diseases in H.
Pylori should be off ered treatment the critical issue is which patients should be tested for the infection strong recommenda-tion quality of evidence. The American Gastroenterological Association AGA has updated its guidance for management of patients refractory to initial eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori. Moderate quality of evidence.
Pylori resistance to antibiotics triple therapy with clarithromycin is no longer the best treatment for H. Not applicable All patients with active peptic ulcer disease PUD a past history of PUD unless previous cure of H. Low quality of evidence for the choice of methods to test for eradication.
The clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of H. Pylori for routine evaluation of dyspepsia or other GI symptoms is not clinically useful or supported by clinical evidence for high prevalence populations For routine clinical practice there is insufficient evidence-based data to support community-wide treatment eradication as a. Pylori infection is identified and treated testing to prove eradication should be performed using a urea breath test fecal antigen test or biopsy-based testing at least 4 weeks after the completion of antibiotic therapy and after PPI therapy has been withheld for 12 weeks.

The Therapy Dose And Cost For Triple And Sequential Therapy Download Table

Phe H Pylori In Dyspepsia Guideline Phe Dh Dwp Guideline Guidelines
How Can Helicobacter Pylori Eradication Therapies Be Improved

Helicobacter Pylori Treatment Regimens Initial Therapies Download Table

Recommended Guidelines For H Pylori Therapy Download Table

H Pylori Infection Treatment Guideline Mpr

Treatment Regimens For H Pylori Eradication In Asia 63 66 Download Table
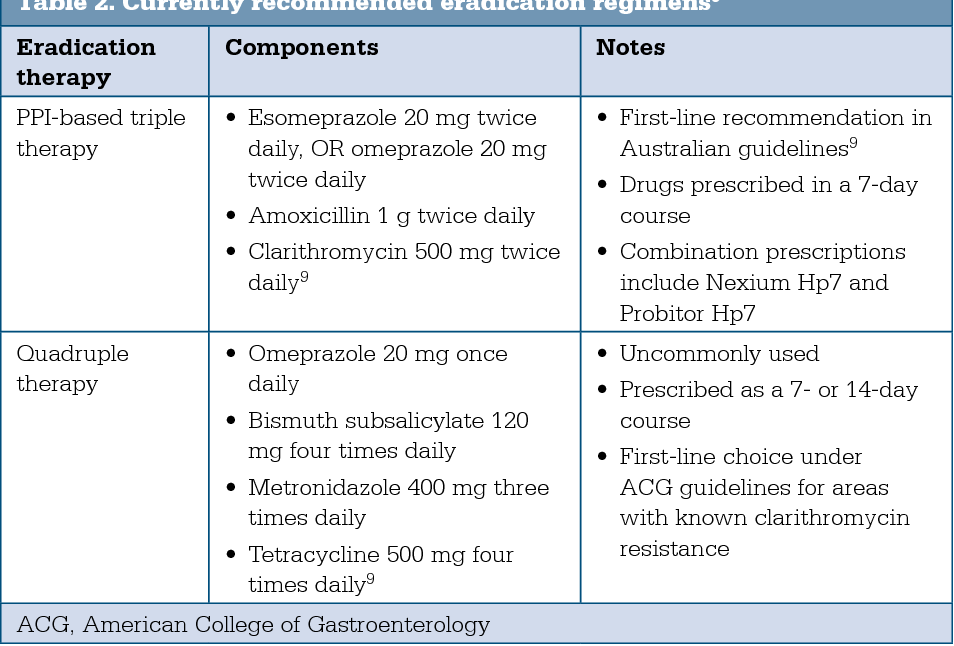
Pdf Helicobacter Pylori Eradication An Update On The Latest Therapies Semantic Scholar

Effective Regimens For Helicobacter Pylori Therapy With Susceptible Download Table
0 comments:
Post a Comment